OZO FHIR implementation guide - Local Development build (v0.5.1) built by the FHIR (HL7® FHIR® Standard) Build Tools. See the Directory of published versions
Authentication Related Person
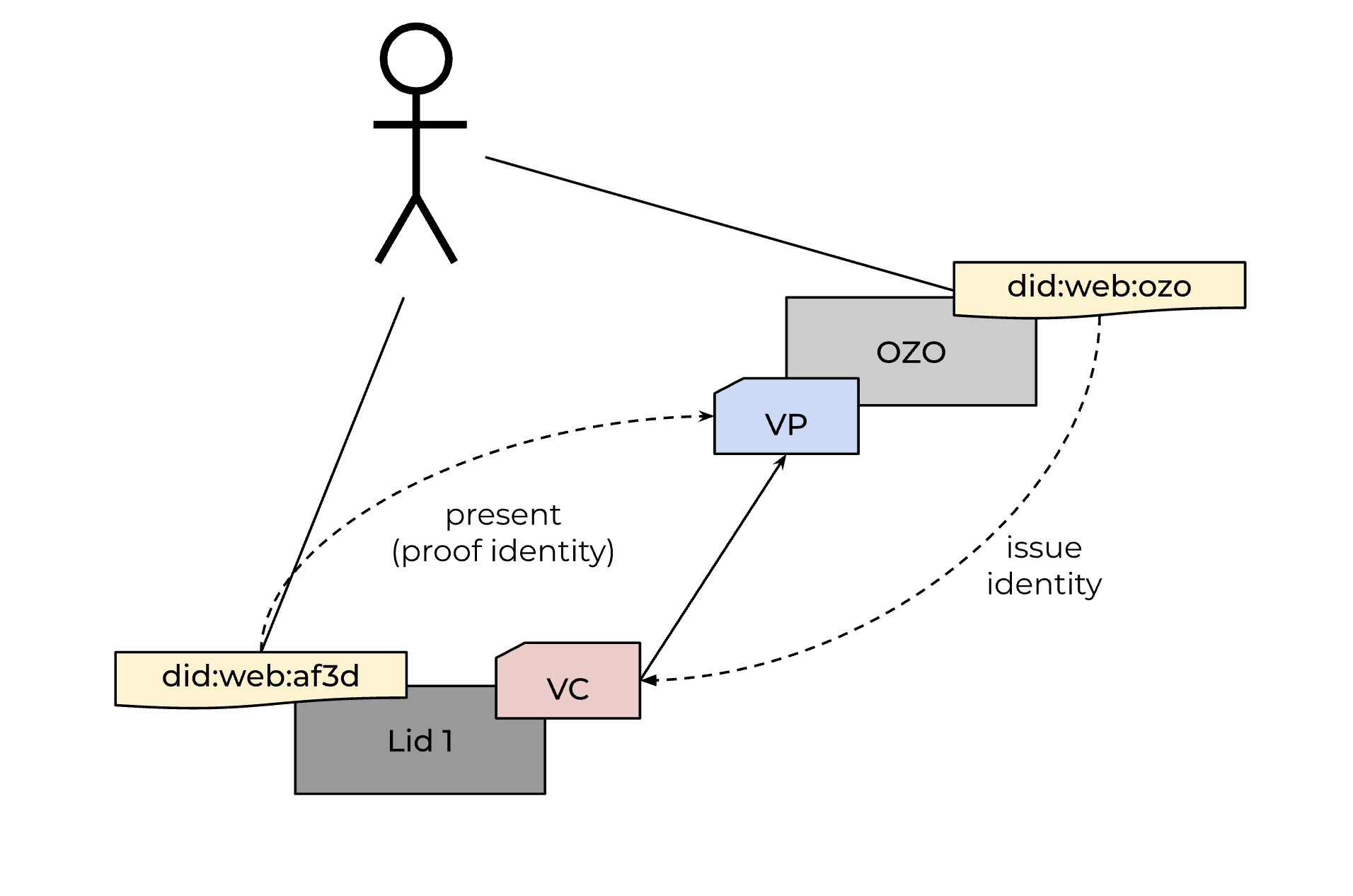
Linking users with OZO can be done by issuing a credential (VC) to the NUTS node of the client application, issued by the OZO did:web, linked to the OZO user, and issued to the user's did:web in the client domain.
This model uses the following credential:
Type: OZOUserCredential
Issuer: another user
Subject: did client user
Explanation of NUTS architecture
Issuance overview
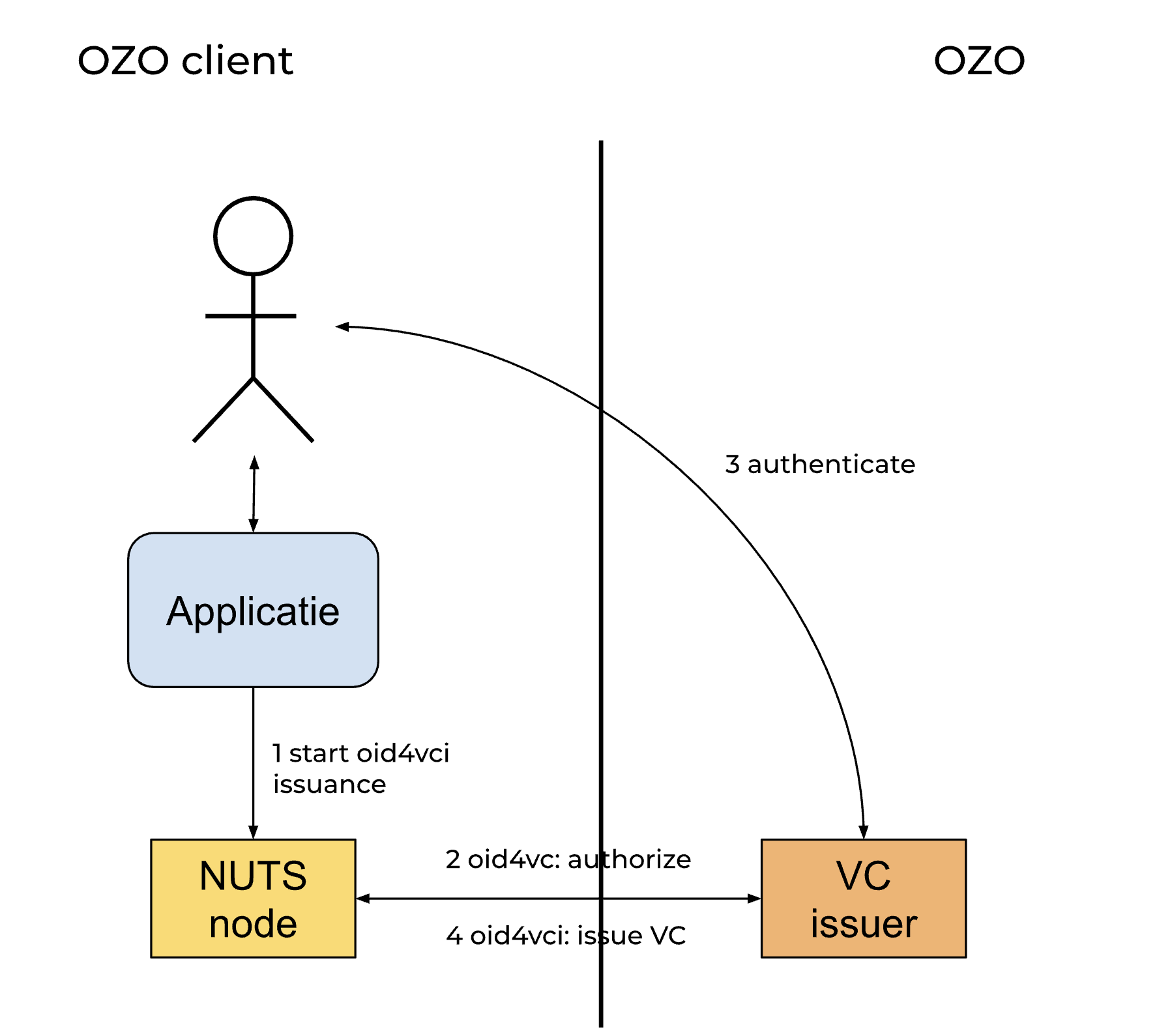
Sequence Diagram Explanation
This diagram illustrates the process of issuing a Verifiable Credential (VC) to a user and accessing an API using that credential. The sequence is divided into two main groups of operations: Issue User Access VC and Access API.
Issue User Access VC
- User Interaction:
- The user initiates interaction with the
client_app.
- The user initiates interaction with the
- Request for VC Issuance:
- The
client_apprequests theclient_nutsto issue a VC by the OID4VCI protocol.
- The
- Engaging with Ozo Issuer:
client_nutssends a request toozo_issuerto issue the VC as part of the OID4VCI protocol.ozo_issuersends an authentication request to the user.- The user responds by providing their credentials to
ozo_issuer.
- VC Creation and Issuance:
ozo_issuercreates the Verifiable Credential using the OID4VCI protocol.- The VC is issued to
client_nutsusing the OID4VCI protocol. client_nutsstores the VC.
- Process Completion:
- The
client_nutsinforms theclient_appthat the process is complete.
- The
This sequence diagram demonstrates how the system manages the process of VC issuance followed by secure resource access using the credential.
Sequence Diagram Explanation
This sequence diagram illustrates the steps involved in obtaining a Verifiable Credential (VC) using the OpenID for Verifiable Credential Issuance (OID4VCI) framework. The interaction involves a user, a client application, a NUTS node client, and an OZO issuer. Here’s a breakdown of the process:
Initial Connection and Configuration
- User Connection:
- The "User Agent" initiates a connection with the
Client applicationto start the credential issuance process.
- The "User Agent" initiates a connection with the
- Issuance Initiation:
- The
Client applicationinstructs theNUTS node clientto start the OID4VCI issuance process for the issuer identified asdid:web:ozo.
- The
- Request Issuer Configuration:
- The
NUTS node clientqueries theOZO issuerfor its OpenID credential issuer configuration file. - The
OZO issuerresponds with its configuration details.
- The
- Discover Authorization Information:
- The
NUTS node clientretrieves a list of authorization servers. - It requests additional OpenID configuration from the
OZO issuer. - The
OZO issuerprovides the necessary configuration information.
- The
- Prepare for User Authorization:
- The
NUTS node clientidentifies the authorization endpoint. - It generates a URL for the authorization redirect, which includes the
redirect_uriand any requiredauthorization_details. - This redirection URL is sent to the
Client application, which then forwards this information to the user.
- The
User Authorization
- Authorization Endpoint Access:
- The user accesses the authorization endpoint through the
OZO issuer. - An authorization page is presented to the user to input their login credentials.
- The user accesses the authorization endpoint through the
- Credential Verification:
- The
OZO issuervalidates the user's credentials. - Upon successful validation, the user is redirected to a specified redirect URI with an authorization code appended.
- The
Credential Issuance
- Obtain an Access Token:
- The user follows the redirect back to the
NUTS node client, providing the authorization code. - The
NUTS node clientexchanges this code for an access token from theOZO issuer.
- The user follows the redirect back to the
- Request Verifiable Credential:
- With the access token, the
NUTS node clientrequests the Verifiable Credential from theOZO issuer. - The
OZO issuergenerates and returns the VC.
- With the access token, the
- Finalizing the Process:
- The
NUTS node clientsecurely stores the VC. - A confirmation message is sent back to the user, indicating successful completion of the VC issuance process.
- The
This structured workflow ensures a secure and reliable end-to-end system for credential issuance, leveraging the capabilities of OpenID for decentralized identity verification.
Access overview
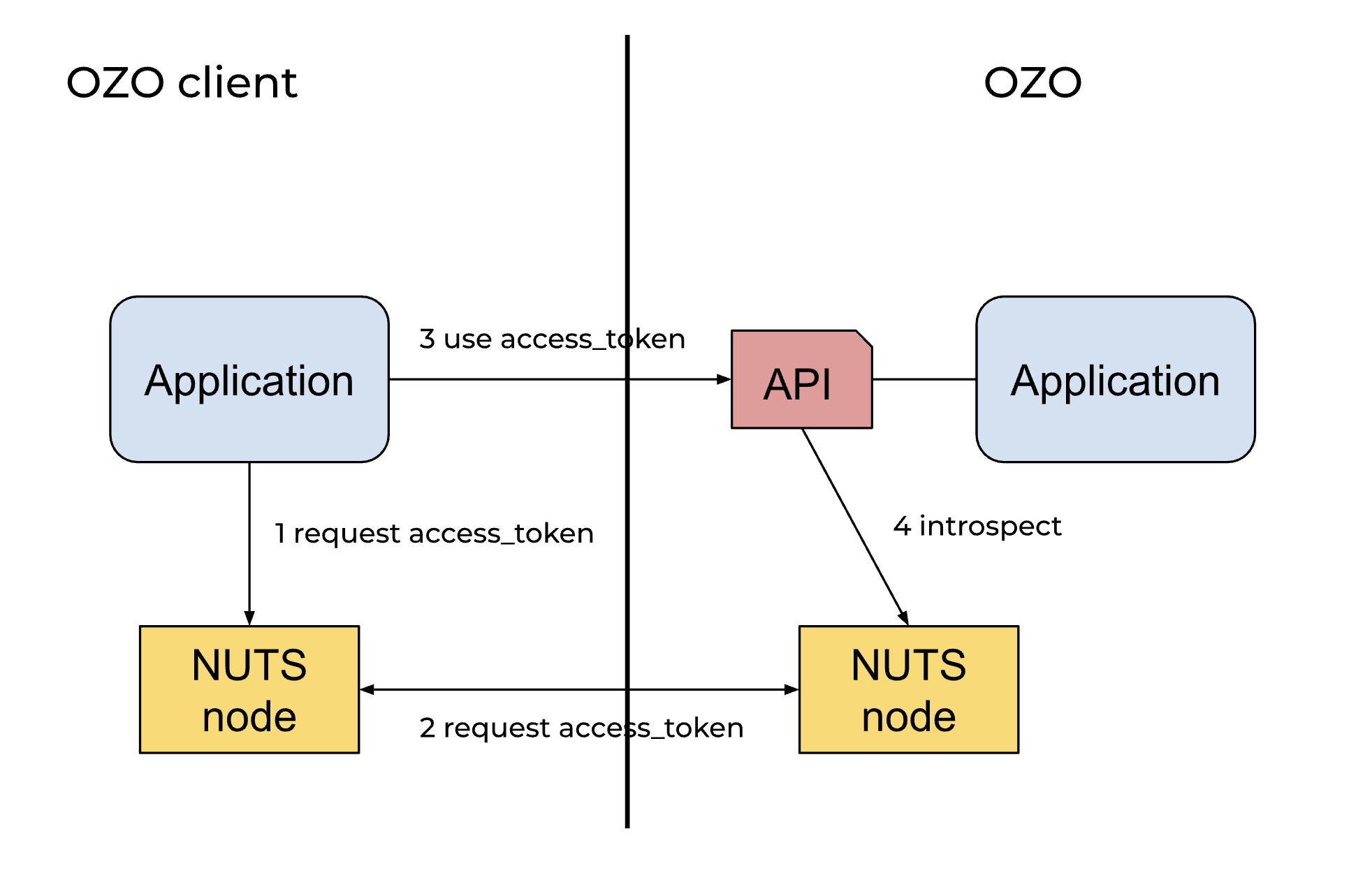
Access to the API is provided in the context of the RelatedPerson that is active in the client application. The NUTS node of the client application holds the secrets that are required to access the OZO API, the link between the logged in user and the subject in the NUTS node needs to be protected.
The procedure of getting access to the OZO api starts with a request towards the NUTS node for an access credential. The NUTS node starts a negotiation with the NUTS node of the OZO platform. As soon as the NUTS node of the client has presented the right Verifiable Credentials in de form of signed Verifiable Presentations, the NUTS node of OZO provides an access_token. The client application uses the access_token to access the OZO API. The OZO Api introspects the access_token and uses the information in the introspection result to apply search narrowing.
UML Sequence Diagram Explanation
Participants
- Client App: Represents the application client which initiates the requests.
- Client NUTS: Acts as a mediator for the client app to interact with other services.
- NUTS OZO: A service that handles the access token creation and validation.
- OZO API: An application boundary that provides endpoints for the client app to access.
Entities
- Access Token: A token used for authentication and authorization.
- DPoP Keypair: A keypair used to generate DPoP tokens.
Process
1. Get Access Token
- Client App sends a request to Client NUTS to get a service access token.
- Client NUTS forwards the request to NUTS OZO to obtain an access token for a specific subject.
- NUTS OZO sends a
presentation_requestback to Client NUTS requiring membership and user credentials. - NUTS OZO creates an access token upon receiving the
presentation_responsefrom Client NUTS containing the required credentials. - NUTS OZO validates the presentation response.
- On successful validation, NUTS OZO sends the generated access token back to Client NUTS.
- Client NUTS creates a DPoP key.
- Client NUTS returns the access token along with a DPoP Key ID (dpop_kid) to the Client App.
2. Use Access Token
- Client App initiates a request to Client NUTS to get a DPoP token.
- Client NUTS signs the request using the DPoP keypair.
- The signed DPoP token is returned to Client App.
- Client App makes an authenticated request to OZO API with the access token and dpop_token.
- OZO API introspects the access token with NUTS OZO.
- NUTS OZO checks the access token's validity.
- On successful validation, NUTS OZO indicates success to OZO API.
- OZO API then introspects the dpop_token with NUTS OZO.
- NUTS OZO verifies the dpop_token.
- On successful verification, NUTS OZO signals success back to OZO API.
- OZO API responds successfully to the Client App with the requested data.
This diagram outlines the flow for obtaining and using an access token with DPoP for secure communication between the client application and the server, illustrating interaction sequences among different participants.